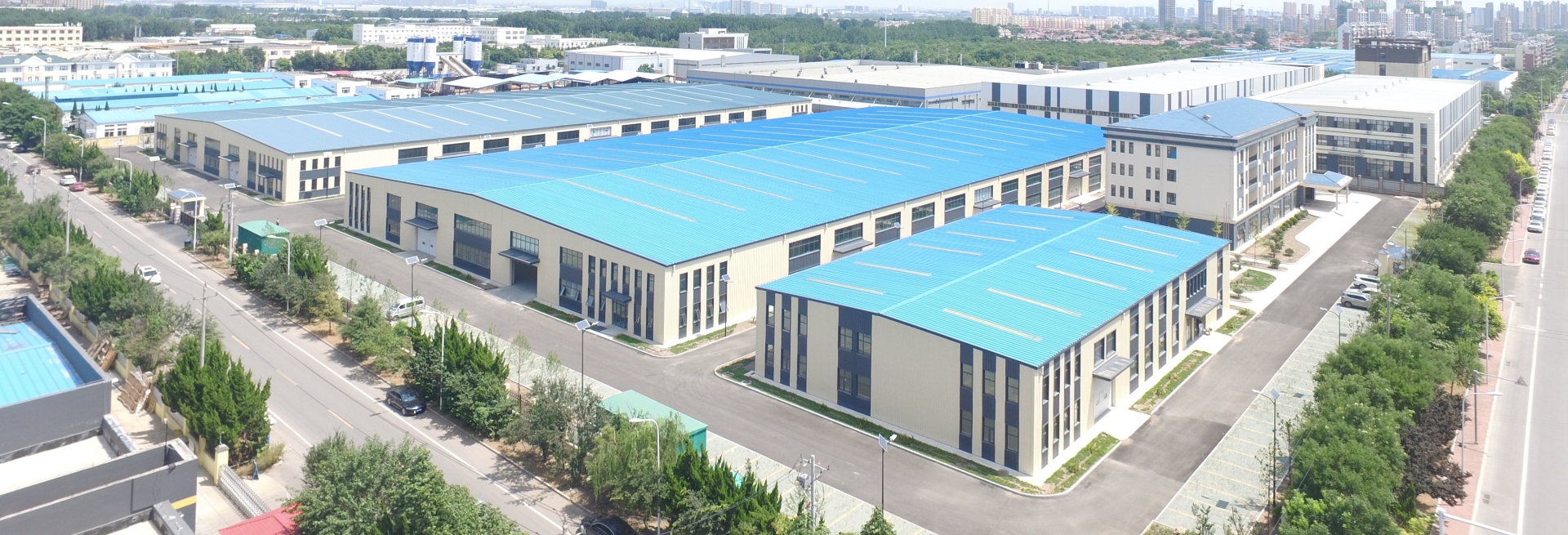
Classification of elastic deformation of fibers
The elastic deformation of fibers can be divided into three categories based on their recovery ability and mechanism of action: rapid elastic deformation, slow elastic deformation, and plastic deformation, which together determine the wearability and durability of textiles.
1. Rapid elastic deformation (reversible elastic deformation)
Rapid elastic deformation refers to the deformation of fibers immediately under external force, and the complete recovery of deformation immediately after the external force is removed. This deformation originates from the changes in bond angles and small segment movements of fiber polymer chains, without consuming energy or generating heat. Spandex can quickly rebound after stretching, making it an ideal material for tight fitting clothing. The range of rapid elastic deformation is usually between 1% and 5%, and beyond this range, it will enter the stage of gradual elastic deformation.
2. Delayed elastic deformation
When the external force is applied for a long time or the deformation is large, the fiber will undergo slow elastic deformation. At this point, the molecular chain segments undergo slippage and rearrangement, and it takes some time to gradually recover after removing external forces.
3. Plastic deformation (permanent deformation)
When the external force exceeds the elastic limit of the fiber, the molecular chain undergoes irreversible displacement and fracture, resulting in permanent deformation. Plastic deformation can reduce the strength and service life of fibers, so tension control is necessary in textile processing to avoid excessive stretching.
-
 Email:wanss@kusan-if.com
Email:wanss@kusan-if.com
-
 website:www.kusan.cn
website:www.kusan.cn
-
 business address one:No. 3, Futai Road, Lancun Town, Jimo District, Qingdao, Shandong business address two:No. 99, Fengjin Road, Shangma Street, Chengyang District, Qingdao, Shandong
business address one:No. 3, Futai Road, Lancun Town, Jimo District, Qingdao, Shandong business address two:No. 99, Fengjin Road, Shangma Street, Chengyang District, Qingdao, Shandong

Scan the code
Copyright © 2020-2030 www.kusan.cn Qingdao Jiushan Textile fabric Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved
website:www.kusan.cn address:No. 3, Futai Road, Lancun Town, Jimo District, Qingdao, Shandong ICP Certificate: ICP Lu No. 20021986-1

 简体中文
简体中文 Japanese
Japanese 한국어
한국어
