Science Popularization - Basic Concepts of General Knowledge
Fabric knowledge covers a series of basic concepts in textiles. It includes a comprehensive understanding and recognition of fabric materials, weaving techniques, fiber types, structural characteristics, and post-treatment technologies. From natural fibers such as cotton, linen, silk, and wool to synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and polyester fibers, each fabric has its unique touch, breathability, moisture absorption, wear resistance, and suitability for various occasions. In addition, different weaving methods, such as plain weave, twill weave, satin weave, etc., can also affect the appearance and performance of the fabric. Fabric knowledge also involves understanding post-processing techniques for fabrics, such as dyeing, printing, coating, waterproofing, etc., which can give fabrics more functionality and beauty. Mastering these fundamental concepts is crucial for selecting suitable fabrics, designing clothing, and conducting fabric innovation.
1. The representation of yarn thickness:
Fixed length system
(1) Danielle (D): It is the weight (in grams) of 9000 meters long, and the larger it is, the thicker the yarn. Generally speaking, Daniel uses' w 'to represent the thickness of synthetic fibers; For example, polyester spinning: 68D * 68D refers to polyester filament with a warp thickness of 68D and a weft thickness of 68D.
(2) Tex (H): The weight (in grams) of a 1000 meter long yarn, therefore, the larger the number, the thicker the yarn. This generally represents the thickness of short fiber yarns; For example, 14.5tex cotton yarn represents 40 inches of cotton yarn. Number is used according to international standards. Generally used more in technical articles and less in industrial articles.
Fixed weight system:
(1) Metric number (N): N=L/G, where G is the weight (grams) of the yarn (or silk), L is the length (meters) of the yarn (or silk), which is a metric number. The unit weight (per kilometer) of the yarn at the given moisture regain is a multiple of one thousand meters. (Often measured in Nm).
(2) English numerals (S): S=L/(G * 840), where G is the weight of the thread (pounds) and L is the length of the thread (yards), as we often say 20, 30, 40, etc. The larger the number, the finer the yarn. Simply put, the length of a unit weight (1 pound) of yarn at a nominal regain is a multiple of 840 yards. A few 840 yards is equivalent to imperial silk yarn. (often represented as Ne). The unit symbol is S.
2. select conversion formula:
(1) The conversion formula for metric numbers (N) and denier (D): D=9000/N
(2) The conversion formula for British numerals (S) and Deniers (D) is D=5315/S
(3) The conversion formula between metric centimeters (cm) and British inches (inch) is: 1 inch=2.54cm
(4) The conversion formula between metric meter (M) and imperial code (yd) is: 1 code=0.9144 meter
-
 Email:wanss@kusan-if.com
Email:wanss@kusan-if.com
-
 website:www.kusan.cn
website:www.kusan.cn
-
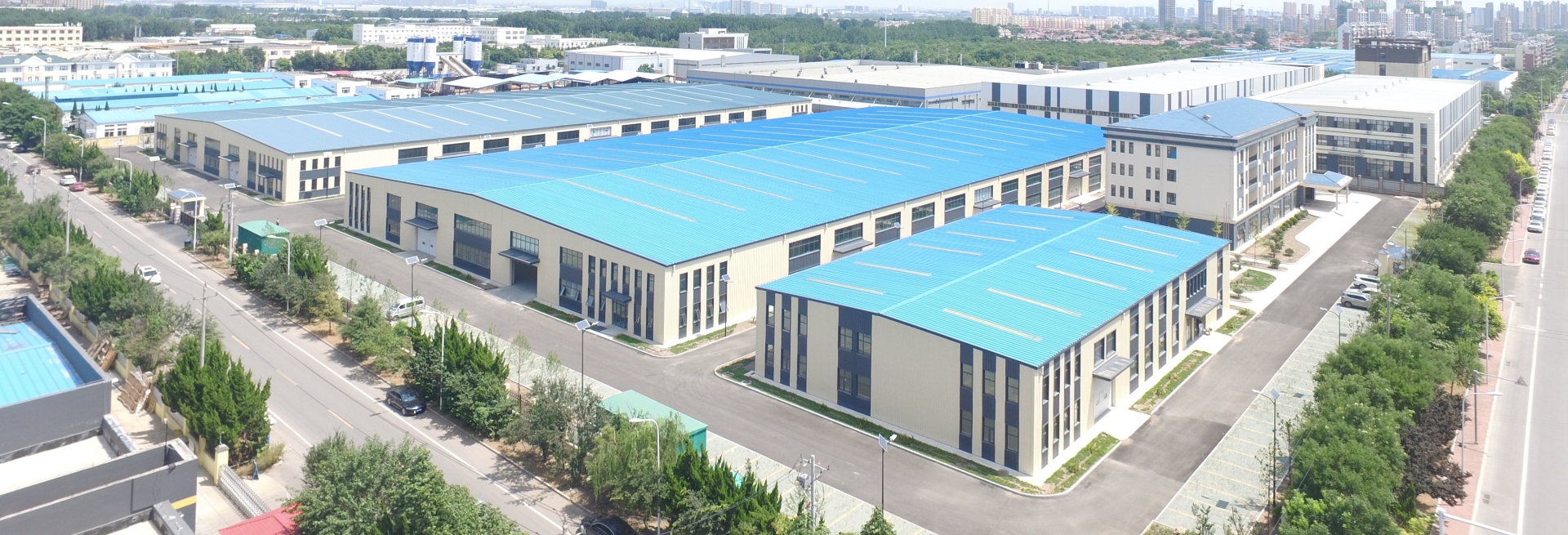
 business address one:No. 3, Futai Road, Lancun Town, Jimo District, Qingdao, Shandong business address two:No. 99, Fengjin Road, Shangma Street, Chengyang District, Qingdao, Shandong
business address one:No. 3, Futai Road, Lancun Town, Jimo District, Qingdao, Shandong business address two:No. 99, Fengjin Road, Shangma Street, Chengyang District, Qingdao, Shandong

Scan the code
Copyright © 2020-2030 www.kusan.cn Qingdao Jiushan Textile fabric Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved
website:www.kusan.cn address:No. 3, Futai Road, Lancun Town, Jimo District, Qingdao, Shandong ICP Certificate: ICP Lu No. 20021986-1

 简体中文
简体中文 Japanese
Japanese 한국어
한국어
